A potentially serious infectious disease called TB (tuberculosis) primarily affects the lungs. Tiny droplets released into the air by sneezing and coughing is responsible for spreading the bacteria that cause tuberculosis from one individual to another. Tuberculosis infection, once rare in Cameroon has been on the rise in recent years, partly due to the advent of HIV virus that result to AIDS. In order to render the immune system of infected people incapable of fighting tuberculosis, the HIV virus weakens the immune system of infected people.
In this article we will discuss tuberculosis as a disease, types of tuberculosis, symptoms, causes and possible tuberculosis treatment types. Bigmanlab Yaoundé Cameroon has seen a slight increase in tuberculosis cases in recent times and so our experts felt the need to explore this disease so as to create awareness and possibly prevent further spreading of the disease.
In Cameroon, TB has remained a national concern as new tuberculosis cases have been slowly rising due to less stringent control programs. Drugs most commonly used to treat tuberculosis have encountered resistance by many tuberculosis strains. To prevent antibiotic resistance and clear the infection, people with active tuberculosis must take several types of drugs for many months.
Is tuberculosis curable?
Tuberculosis was one of the major causes of death in Cameroon. Some antibiotics though may take long time, can treat tuberculosis. You must take drugs for 6-9 months at least.
Is tuberculosis common?
About 1.5 million people died from tuberculosis and about 10 million people contracted the disease worldwide in 2020. TB was once the leading cause of death in the United States, according to the CDC.
What about tuberculosis transmission?
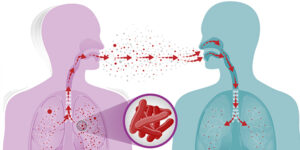
When a person with tuberculosis in the throat or lungs sings, coughs, talks, or sneezes, tuberculosis germs are released into the air. Depending on the environment, these germs can survive in the air for many hours. You can be infected if you breathe air that contains tuberculosis germs; a condition known as latent tuberculosis infection.
What about tuberculosis symptoms?
Your immune system can usually keep you from getting sick even though your body can harbor tuberculosis bacteria. Health care provider for this reason distinguish between:
Active tuberculosis:
In most active tuberculosis cases the infection can be passed on to other people, results to sickness, and is equally called tuberculosis disease. It can appear years or weeks after tuberculosis bacterial infection.
Latent tuberculosis:
The bacteria in your body do not cause any symptoms and are inactive even though you have the tuberculosis infection. Tuberculosis infection, also called latent tuberculosis or inactive tuberculosis, is not contagious.
Treatment is essential with latent tuberculosis since it can turn into active tuberculosis.
The typical tuberculosis symptoms are:
- Neck swelling.
- Loss of weight.
- Fatigue and tiredness.
- Elevated temperature.
- Sweating at night.
- Appetite loss.
- 3 weeks of persistent coughing and sometimes produces phlegm that may even be bloody.
If you cough up blood or if your cough lasts more than 3 weeks then call your healthcare provider for testing, diagnosis and treatment.
What about tuberculosis causes?
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by a bacterial. Usually, the most contagious tuberculosis type known as pulmonary tuberculosis (which affects the lungs), only spreads only after prolonged contact with someone who has the tuberculosis. Tuberculosis in most healthy people causes no symptoms and the immune system (the body’s natural line of defense against illnesses and infection) kills the bacteria.
The immune system sometimes stops tuberculosis from spreading throughout the body since it can't kill the bacteria. The bacteria will still be in your body even though you will have no symptoms. This condition is called latent tuberculosis. Latent tuberculosis infected people are not contagious to other people.
Symptoms developing over months or weeks if the immune system does not clear or contain the infection and the disease can spread to other parts of the body including the lungs. A condition referred to as active tuberculosis. Especially if the immune system is compromised latent TB can later in life develop into active TB disease.
What about risk factors of tuberculosis?
- You are more likely to have tuberculosis if:
- Family member, colleague, or friend has active tuberculosis.
- Traveled or live in a tuberculosis infested area, such as the Caribbean Russia, Latin America, Eastern Europe, Asia and Africa.
- You live or work with someone who has TB or you are in a group where tuberculosis is more likely to be transmitted. This includes people who inject drugs into their veins, people in jail or prisons, people living with
- HIV and the homeless.
- You live or work in a nursing home or hospital.
- Jobs in the health sector for patients at high tuberculosis risk.
- You smoke.
Tuberculosis bacteria can be fought by a healthy immune system. But active tuberculosis cannot be prevent if you have:
- AIDS or HIV.
- Diabetic.
- Organ Transplant Drugs
- Serious kidney disease.
- Neck and head cancer.
- Some medications used to treat psoriasis, Crohn's disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Chemotherapy cancer treatments.
- Poor diet and low body weight.
Because the immune systems young children and babies are not yet fully formed, they are also more likely to be affected.
What about tuberculosis prevention?
Before you pick up tuberculosis you sometimes have to be around someone with active tuberculosis for a long time. It is helpful to follow guidelines for infection prevention, such as:
- Until cleared by your doctor, do not return to school or work.
- Cover your mouth when you cough or cough into your elbow.
- Stay further away from infected people.
- Thoroughly often wash your hands.
- Ensure you correctly take all your medicines.
- Use of the correct type of personal protective equipment and good ventilation are the most essential actions to stop the tuberculosis spread in hospital settings.
What about tuberculosis treatment?
Tuberculosis treatment will depend on infection type.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe one or more different medicines if you have drug-resistant tuberculosis. It may cause more side effects but you may need to take it up to 30 months or for longer.
Your healthcare provider will give you medicine to kill the bacteria if you have latent tuberculosis, so that the infection does not become active. Alone or in combination, you may be given rifampin, rifapentine, or isoniazid. You should consume the drug for up to about 9 months. Contact your doctor immediately if you see active tuberculosis signs.
Active tuberculosis can equally be treated by a combination drugs. The most familiar are pyrazinamide, isoniazid, rifampicin, and ethambutol. You will take it for 6-12 months.
It is important to finish all of your medications regardless of the type of infection you have, even if you feel much better. The bacteria can become resistant to the medicine if it is stopped too soon.
What about tuberculosis vaccination
In Cameroon where tuberculosis is quite common, children often receive the BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guerin) vaccines. The Bacille Calmette-Guerin vaccine is not recommended for general use in the west as it is not very effective in some adults. Dozens of new tuberculosis vaccines are in various stages of testing and development.
Bigmanlab Statement on tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is an airborne infection. Although treatable, this disease is still responsible for several deaths in Cameroon. We recommend you contact your healthcare provider if you think you have tuberculosis symptoms or have been exposed to tuberculosis. Equally, be sure to follow the instructions if you are receiving tuberculosis treatment. Contact bigmanlab if you have any more questions.







