Syphilis disease is a sexually transmissible bacterial infection (STI). This sexually transmissible disease begins usually on the rectum, mouth, or genitals as a painless ulcer. Through mucous or skin membrane contacts between these sores, Syphilis is transmitted from person to person. The bacteria that causes syphilis can remain dormant in the body after the initial infection for several years before reactivating.
Sometimes with a single penicillin shot, early syphilis infection is curable. Without proper syphilis treatment, it can be life-threatening, damage the brain, and other body organs and seriously damage the heart. Mother can equally transmit Syphilis to babies.
What is syphilis disease?
Syphilis disease is an STI that can cause serious problems to health if left untreated. The syphilis infection develops gradually from primary to secondary to latent and tertiary stages. Different signs and symptoms can be seen in each stage. And the bigmanlab has over the years carried out in-depth research into these stage for better understanding of the syphilis disease.
What are the stages of syphilis disease?
Four different stages exist through which Syphilis can progress. At each stage, the infection causes different symptoms. Humans are highly contagious at stages one and two and can likely transmit the bacteria infection on to their sexual partners.
The stages of syphilis infection are: primary stage, secondary stage, latent stage, and tertiary (advanced) syphilis stage.
Primary syphilis disease stage:
The very first sign of this disease is a little body sore (chancre). The place where the syphilis bacteria goes into your body is where the sores appears. While most infected people develop more than one sore, most individuals develop just one. The sore commonly develops around 3 weeks after you’re exposed to the bacteria. Because the chancre is often painless and can hide in the rectum or vagina, a lot of people with syphilis do not notice it. Within three to six weeks the syphilis sore will self-heal.
Secondary syphilis stage:
You may develop rashes that starts on your body trunk within a few weeks of being cured of the original sore but it soon fills your whole body, including the soles of the feet and palms of the hands. This rash may appear alongside some wart-like ulcers in the genitals or mouth and is usually not itchy. Some people equally experience sore throat, fever, lymph nodes that is swollen, hair loss and body aches. These syphilis symptoms and signs may appear and disappear repeatedly for up to a year or go away in a few weeks.
Latent syphilis stage:
The disease progresses from the syphilis secondary phase to the secret (latent) stage if you don't get treatment for syphilis, and here you don’t experience any symptoms. The stage syphilis phase can last up to years. Syphilis symptoms and signs may not appear again or the syphilis disease may pass on to stage three (tertiary).
Tertiary syphilis stage:
Complications termed as tertiary syphilis phase will appear usually in about 15% - 30% of infected people who do not receive proper treatment. This disease can damage the joints, nerves, eyes, bones, blood vessels, brain, liver and heart in advanced stages. This issue can appear years right after the initial untreated syphilis infection.
Causes of syphilis disease
The bacterium Treponema pallidum causes Syphilis disease. By direct contact with syphilitic sores on the body of another person, syphilis is obtained. The bacteria can also enter the body via mucous membranes or through breaks in the skin, but usually infection occurs during sexual activity. Syphilis cannot be transmitted from eating utensils, doorknobs, swimming pools, shared clothing, bathtubs, toilet seats or hot tubs.
Who is at higher risk of contracting syphilis disease?
Some factors can boost your chances of getting infected, but basically anyone can get syphilis disease.
People at increased risk of contracting syphilis disease are:
- HIV infected people.
- Same sex intercourse people.
- People who have sex with multiple partners without a barrier method, such as a condom.
- People with syphilis infected sexual partners.
How to reduce the risk of syphilis disease?
Not having anal, oral, or vaginal sex is the only way to completely avoid STI (syphilis).
You can do the following to reduce your chances of getting syphilis if you are sexually active:
- Use protection correctly during sex.
- Avoid drugs. Abuse of alcohol or other recreational drugs can lead to unsafe sexual practices by impairing your judgment.
- Staying with a proven syphilis-free partner in a long-term monogamous relationship.
Avoid contact with the sores by using condoms which also serves to prevent the spread of syphilis disease. Contact with sores that appear on areas not covered with condoms can still result in the spread of syphilis.
Contact bigmanlab if:
- You inject the medication with a needle used by someone who may have syphilis.
- Your sexual partners have told you that they have another sexually transmitted infection (STI) or syphilis.
- Plan to become pregnant or are pregnant and think you are at risk.
- You recently had sex with a new partner and you haven't used a condom
- Your sexual partner or you a have syphilis symptoms.
A test is the only way to know if you have syphilis infection. Syphilis treatment should be started as soon as possible if test is positive for syphilis infection.
To verify if you’re having syphilis
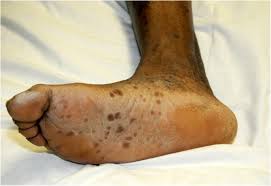
The syphilis symptoms are usually mild and difficult to notice. They tend to come and go and can change over time.
Syphilis symptoms include:
- Small ulcers (sores) around the buttocks (anus), on the vagina or penis - you may only have one and they are usually painless.
- Ulcers in other areas, like on the lips or the mouth or buttocks or hands
- Gray or white wart growths most often around the anus, vagina or on the penis.
- A rash on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands (this is usually not an itch), which can sometimes spread over the entire body
- Inflamed glands
- White mouth patches.
- Flu-like syphilis symptoms, like as tiredness, headache, and fever.
- Patchy hair loss on eyebrows, beard, and on the head.
After syphilis infection, symptoms can take up to 3 weeks or longer to appear. If symptoms haven't been treated, the infection is still in your body but sometimes the symptoms go away or improve. This means that you’re at serious risk later on and can still transmit it.
Syphilis Complications
Conditions with the liver, testicles, skin, bones, and other organs
Syphilis can cause some serious life-threatening problems if left untreated, these include:
- Brain condition such as dementia seizures, personality changes, and memory problems.
- Heart conditions like as heart failure, angina and aortic aneurysm.
- Nerve conditions like gradual damage to the joins, joint pains needles and pins, and shooting pains.
Most of these complications of syphilis may not appear for several years after contracting a syphilis infection.
What about congenital syphilis?
During pregnancy, when woman transmits the bacteria infection to her fetus, this is known as congenital syphilis. Syphilis can cause even death in babies and other serious health problems little children. At one of her first prenatal visits, a pregnancy care provider should check you for STIs. If you test positive for syphilis, it’s very important to get treatment immediately.
Syphilis during pregnancy
A health care provider should check for syphilis disease and all sexually transmitted infections (STIs) during the first trimester, as part of her routine prenatal care if you’re pregnant. Increase the risk of pregnancy complications, like stillbirth, premature birth, and miscarriage, can be associated to STIs.
Because syphilis is transmitted to the child during pregnancy, it is equally part of what your health care provider looks for. A situation known as congenital syphilis. Serious harm to newborns that can even be life-threatening can result from untreated congenital syphilis.
Syphilis infected pregnant women almost always pass syphilis to their babies. For this reason, treating syphilis during pregnancy is essential to protect your baby’s health and yours too.
Babies born through congenital syphilis may develop:
- Jaundice
- Delay in development
- High fever
- Infectious ulcers
- Regular seizures
- Body rash
- Swollen spleen or liver
- Severe anemia
Late-stage syphilis can result from untreated congenital syphilis. These can harm your baby’s: Brain, eyes, ears, bones, and teeth.
Syphilis during pregnancy is mostly treated with penicillin. For those with penicillin allergies, the health care provider may take a few hours to administer the drug. This give your body more time to receive a small dose of the drug that doesn’t cause allergies.
Syphilis treatment
Antibiotics which can be obtained as capsules, tablets, or injections can be used to treat syphilis. Treatment can begin before test results are known. Penicillin allergic people will likely be treated with other types of antibiotics, like:
- Ceftriaxone
- Doxycycline
The stage of your syphilis determines the duration of your treatment. In some people, the medicines can cause flu-like symptoms, like body aches, headache, and high fever. This often takes up to 24 hours. Six and 12 weeks after starting treatment retest with your health care provider.
Is syphilis disease completely curable?
The answer is yes! With antibiotics your doctor can treat syphilis. Though the antibiotics cure the infection, it’s not possible to repair damaged organs.
Message about syphilis from the bigmanlab team of experts
Do not panic when you have syphilis, Syphilis is a treatable STI. In order to receive early treatment, in the early stages of the bacteria infection, it is important to get tested early. Long-term health problems may result from untreated syphilis. Have a very honest conversation with your doctor about your sexual life. Your doctor can help you understand the risks, take possible preventive measures, and develop a plan for you to remain in good health.